Do you want to know more about diabetes mellitus , its causes , types and other characteristics which makes this disease more common in coming generations ?
You are on the right page where we will specify all the aspects, problems and characteristics of this disease in a detailed way and try to enlighten you with full knowledge of Diabetes mellitus and how to properly handle this disease and else manage this disease for your loved ones.
Introduction :
Diabetes is a condition in which a person gets panic and thinks what will happen next and increases his/her mental pressure and feels like a very kind condition. But hey don’t worry and just try to manage your situation very carefully and try to recover as soon as possible by doing right amount and type of exercises and maintaining your diet in a very discipline manner.

Here below we are going to discus important topics one by on which you can find in table of content given in starting of the blog.
Definition of Diabetes
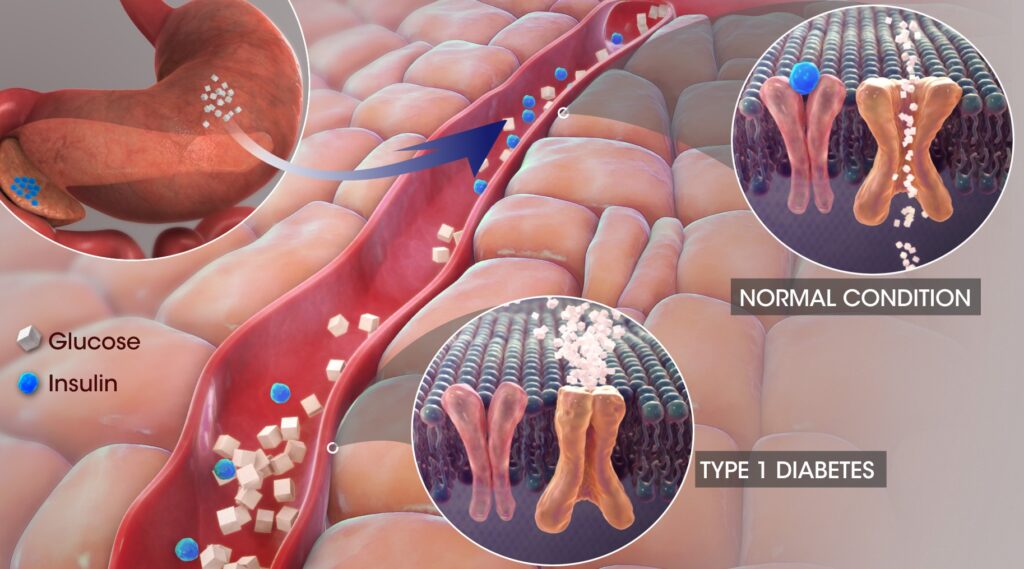
Diabetes mellitus is a group of some metabolic disorder in which level of glucose increases in our blood stream due to either no secretion of insulin which maintains the balance of glucose level in blood and cells or no function of insulin which is released from pancreas which also causes imbalance of glucose level.
Classification :
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects the way the body uses, produces, and stores glucose. It is caused by a deficiency in the production of insulin or the body’s inability to use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps the body break down and absorb glucose from food. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, where it cannot be used for energy. Diabetes mellitus is classified into two major types: type 1 DM (T1DM) and type 2 DM (T2DM).
T1DM is an auto-immune disorder in which the body’s own immune system destroys the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas, leading to a complete lack of insulin. T2DM is caused by either a decrease in the body’s ability to produce insulin or an increase in the body’s resistance to the effects of insulin.
The most common symptoms of diabetes mellitus include increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow wound healing. If left untreated, diabetes can lead to chronic complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, nerve damage, and blindness.
Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is typically done through a blood test that measures the amount of sugar in the blood. A diagnosis of T1DM is usually made when an individual has a blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher, while a diagnosis of T2DM is made when an individual has a blood sugar level of 100 mg/dL or higher.
Treatment for diabetes mellitus typically involves lifestyle changes such as increasing physical activity, eating a healthy diet, and monitoring blood sugar levels. In some cases, medications may also be prescribed. These medications can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications from diabetes. In conclusion, diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects the way the body uses and stores glucose. It is caused by a deficiency in the production of insulin or an increase in the body’s resistance to the effects of insulin.
Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow wound healing. Treatment typically involves lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medications to help control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Type 1 Diabetes :
Type 1 condition is a chronic and life-threatening condition in which the body is unable to produce enough insulin to meet its needs. It is an autoimmune disorder that causes the body’s immune system to mistakenly attack and destroy the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Without insulin, the body cannot process glucose, the main source of energy for the body, and instead it breaks down other molecules for energy. People with type 1 diabetes must take insulin injections or use an insulin pump to help manage their condition. They also need to carefully monitor their blood glucose levels, follow a healthy diet, and exercise regularly to help maintain their health. Complications of type 1 diabetes can include kidney damage, nerve damage, and cardiovascular disease.
Other complications can include vision loss, depression, and skin infections. People with type 1 diabetes are also at an increased risk of developing other autoimmune disorders. People with type 1 diabetes can lead full and active lives with proper management. Education, support, and self-management are important components of managing the condition. People with type 1 diabetes should meet with their healthcare team regularly to discuss their condition and stay up to date with the latest treatments.
Type 2 Diabetes :
Type 2 diabetes alters and affects the way our body process glucose or sugar. Muscles and tissues need energy to perform activity and that is provided by glucose. When someone has type 2 diabetes, their body does not make enough insulin, or the body does not use insulin appropriately. This causes the level of glucose in the blood to become too high.
Type 2 condition is the most common form of diabetes and usually occurs in adults over the age of forty. It is a lifelong condition that cannot be cured, but it can be managed. People with type 2 diabetes are at an increased risk for several serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
Managing type 2 diabetes involves making lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, being physically active, and monitoring glucose levels. To control blood sugar level , medication should be an important part. It is important for people with type 2 diabetes to visit their doctor regularly to get blood tests and monitor their health.
People with type 2 condition need to take active steps to prevent or delay the onset of complications. These include getting regular physical activity, monitoring blood sugar levels, taking medications as prescribed, and eating a healthy diet. By taking the right steps, people with type 2 diabetes can help control their condition and live a healthy, full life.
Causes of Diabetes :
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder caused by a number of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental influences. It is characterized by a chronic high level of blood glucose, also known as hyperglycemia, resulting from defects in the body’s ability to produce or use insulin.

The most common type of diabetes is Type 2, which is caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, including obesity and sedentary lifestyle. Insulin resistance, a condition in which the body does not respond to insulin properly, is also a major cause of Type 2 diabetes.
In Type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin, resulting in an inability to regulate blood glucose levels properly. This type of diabetes is typically caused by an autoimmune response, in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the beta cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain toxins and chemicals, can also lead to diabetes. Additionally, certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can increase the risk of developing diabetes. In some cases, diabetes may be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
For example, if someone has a family history of diabetes and is overweight, this may increase their risk of developing the condition. Regardless of the cause, diabetes can have serious health consequences. It can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, as well as other serious complications, such as blindness, kidney failure, and nerve damage. Managing diabetes requires lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking medications to control blood glucose levels.
Symptoms :

1. Excessive Thirst: One of the most common symptoms of diabetes is feeling constantly thirsty. This is because when there is too much sugar in the blood, it causes dehydration.
2. Weight Loss: Another symptom of diabetes is frequent and unexplained weight loss. This is because the body is unable to properly process and store glucose, causing the body to break down fat and muscle tissue for energy.
3. Increase in Urination: People with diabetes may find themselves urinating more frequently, especially at night. This is because the body is trying to get rid of excess sugar in the blood by passing it through the urine.
4. Hunger: People with diabetes may often feel hungry, even after eating a meal. This is because the body is unable to properly absorb and use the glucose from food.
5. Feeling Tired: The body uses glucose to produce energy, so when the body is unable to process and use glucose properly, it can result in feeling fatigued and weak.
6. Blurred Vision: Diabetes can cause the lens of the eye to swell, which can blur the vision. This symptom can be treated with eye drops or glasses.
7. Slow Healing Wounds: People with diabetes may find that cuts and wounds take longer to heal. This is because blood sugar levels can affect the body’s ability to produce collagen and other proteins that are necessary for healing.
8. Yeast Infections: People with diabetes may be more prone to developing yeast infections, as high blood sugar levels can provide the ideal environment for yeast to thrive.
9. Numbness in Limbs: Diabetes can cause a decrease in blood circulation, which can result in numbness or tingling in the extremities.
10. Frequent Infections: High blood sugar levels can also reduce the body’s ability to fight off infections, leading to frequent and recurring infections.
Treatment :
1. Diabetes is a chronic, lifelong condition that is caused by high levels of sugar in the blood. It can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, blindness, and nerve damage.
2. Treatment for diabetes includes lifestyle changes such as eating healthy, exercising, and managing stress.
3. Medications such as insulin, sulfonylureas, meglitinides, and thiazolidinediones are used to help control blood sugar levels.
4. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use glucose for energy. It can be taken as an injection or through an insulin pump.
5. Sulfonylureas help the body make more insulin when needed.
6. Meglitinides help the body use glucose more efficiently.
7. Thiazolidinediones help the body make more insulin and reduce glucose production in the liver.
8. Other medications such as incretin mimetics, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, bile acid sequestrants, and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors can also be used to help control blood sugar levels.
9. Eating a balanced diet that is low in processed foods, high in fiber, and rich in fruits and vegetables is important for managing diabetes.
10. Regular exercise is also important for diabetes management. Exercise helps to reduce stress and manage blood sugar levels.
Precautions :
1. Keep blood sugar levels in check by regularly testing your blood glucose levels.
2. Eat a healthy diet that is low in fat, salt and sugar and high in fiber.
3. Exercise regularly to help regulate your blood sugar levels.
4. Control your weight and follow a weight loss plan if you are overweight.
5. Monitor your feet daily for any cuts, blisters, or other signs of injury.
6. Wear diabetic shoes or use protective inserts to protect your feet.
7. Avoid smoking as it can increase your risk of developing complications.
8. Check your blood pressure regularly as high blood pressure can lead to complications.
9. Wear sunscreen while outdoors to protect your skin from sun damage.
10. Regularly visit your doctor for check-ups to discuss any changes in your condition.
Physiotherapy in Diabetes :
it is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood due to either decreased production of insulin or inability of the body to effectively use the insulin produced. People with diabetes often experience a number of physical, mental and emotional health problems.
Physiotherapy is one of the most important treatments for people with this condition as it helps to improve and maintain their physical, mental and emotional health. Physiotherapy helps to improve the overall physical functioning of people with diabetes. It helps to maintain and improve the range of motion of joints, flexibility, coordination and balance. Strengthening exercises help to improve muscle strength, endurance, and reduce the risk of falls.

Aerobic exercise and resistance training help to improve the overall fitness, cardiovascular health and muscle strength. Exercise also helps to reduce the risk of developing type 2 condition. Physiotherapy plays an important role in the management of diabetes related complications. People with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing various musculoskeletal complications such as diabetic neuropathy, which can lead to loss of sensation and strength.
Physiotherapy helps to reduce the risk of developing these complications by providing regular exercise and strengthening programs. Physiotherapy also helps to reduce the risk of developing secondary complications of this disease.
Exercises for Diabetes :
Diabetes can be managed through lifestyle changes, including regular physical activity, healthy eating, and stress management. Physiotherapy exercises are one part of a comprehensive lifestyle plan to help manage diabetes. Physiotherapy exercises can help improve strength, flexibility, stability, and balance. Regular exercise can also help to reduce blood glucose levels, lower blood pressure, improve circulation, and reduce stress.
- Leg extensions: This exercise helps to improve leg strength and flexibility. Start by lying down on the floor with your legs extended, and then slowly lift one leg off the floor. Hold and slowly take it back. Do 10 repetitions everyday in morning.
- Calf raises: This exercise helps to improve calf strength and stability. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and then slowly rise up onto your toes, raising your heels off the ground. Hold it for a few seconds and then bring your heels back slowly. Do this for 10 repetitions.
- Chair squats: This exercise helps to improve leg strength and stability. Start by sitting in a chair with your feet flat on the floor. Slowly stand up, and then slowly lower yourself back down into the chair. Do this for 10 repetitions.
- Wall push-ups: This exercise helps to improve chest and arm strength. Start by standing with your hands on a wall in front of you and your feet shoulder-width apart. Slowly lower your body towards the wall, and then push yourself back up. Do this for 10 repetitions.
- Walking: This exercise helps to improve overall fitness and endurance. Start by walking at a steady pace for at least 10 minutes. You can increase the intensity of your walking as your fitness improves.
- Stretching: This exercise helps to improve flexibility and range of motion. Start by stretching each muscle group for 10-30 seconds. Focus on stretching the major muscle groups including the chest, shoulders, arms, back, legs, and hips.
These are just a few of the many physiotherapy exercises that can help to manage this condition. Please consult your doctor or physiotherapy before starting any exercise sessions.. With regular exercise, you can help to manage your diabetes and improve your overall health and well-being.
Read more about health conditions here !
Conclusion :
it is a serious condition that can cause long-term health complications if it is not managed properly. People with diabetes should work with their healthcare provider to develop an individualized diabetes management plan to help manage their diabetes and prevent complications.
This plan should include lifestyle modifications such as healthy eating and physical activity, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. The goal of diabetes management is to keep blood glucose levels within a target range to prevent or delay the onset of complications.
