Introduction
Multiple Sclerosis, or MS, is a chronic condition that affects the central nervous system and can have a profound impact on an individual’s quality of life. Despite being a relatively common condition, many people remain unaware of what MS is, its causes, and its symptoms. This guide is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of Multiple Sclerosis for those who are new to the topic.

Whether you or a loved one has recently been diagnosed with MS, or you simply want to learn more about this condition, this guide will provide you with the information you need to understand MS and take the first steps towards managing it.
From exploring the symptoms and causes of Multiple Sclerosis, to discussing available treatments and support resources, this beginner’s guide to Multiple Sclerosis is the perfect starting point for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge and understanding of this complex condition.
Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis is a condition that affects the central nervous system, and as a result, can cause a wide range of symptoms. Some common symptoms of multiple sclerosis are :
- Numbness or tingling in the limbs
- Muscle weakness or spasms
- Vision problems, including double vision or partial blindness
- Problems with balance and coordination
- Fatigue and exhaustion
- Problems with memory and concentration
- Mood swings and depression
It’s important to note that Multiple Sclerosis symptoms can vary greatly from person to person, and can range from mild to severe. Some individuals may experience only mild symptoms, while others may experience severe disability. In some cases, symptoms may come and go, while in other cases, they may progress over time.
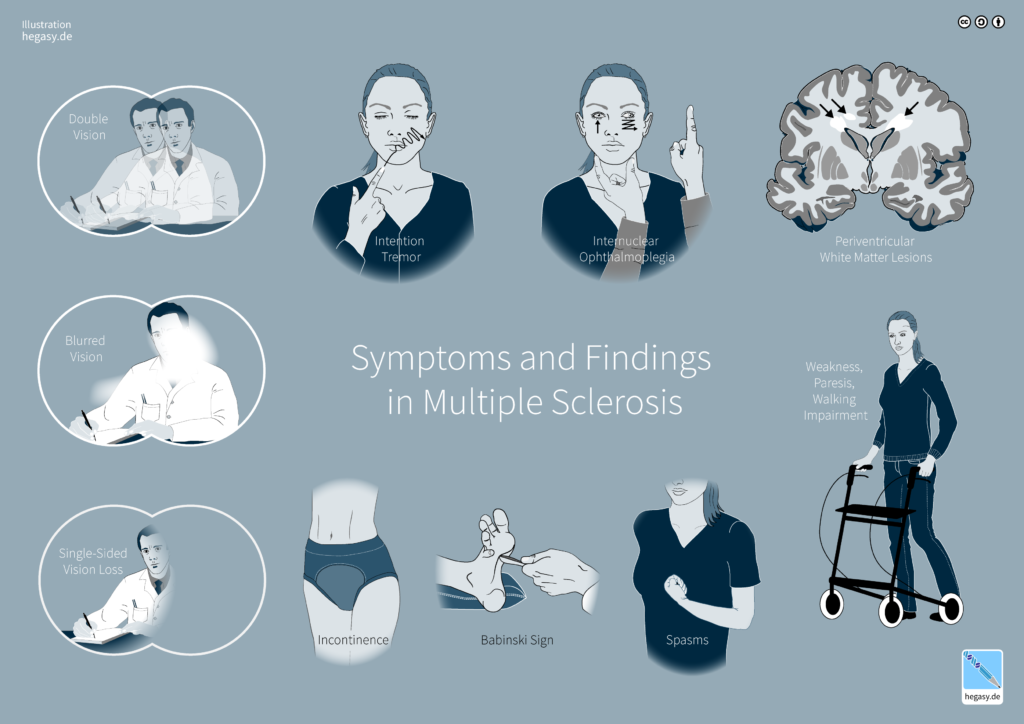
If you suspect you may have MS, it’s important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Your doctor can perform tests to determine the cause of your symptoms and provide you with a proper diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment can help slow the progression of Multiple Sclerosis and improve your overall quality of life.
Causes
The exact cause of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is still not fully understood, but researchers believe that it may be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the factors that are thought to contribute to the development of MS include:
- Genetics: MS is more common in people with a family history of the condition.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain viruses or other environmental triggers may increase the risk of developing MS.
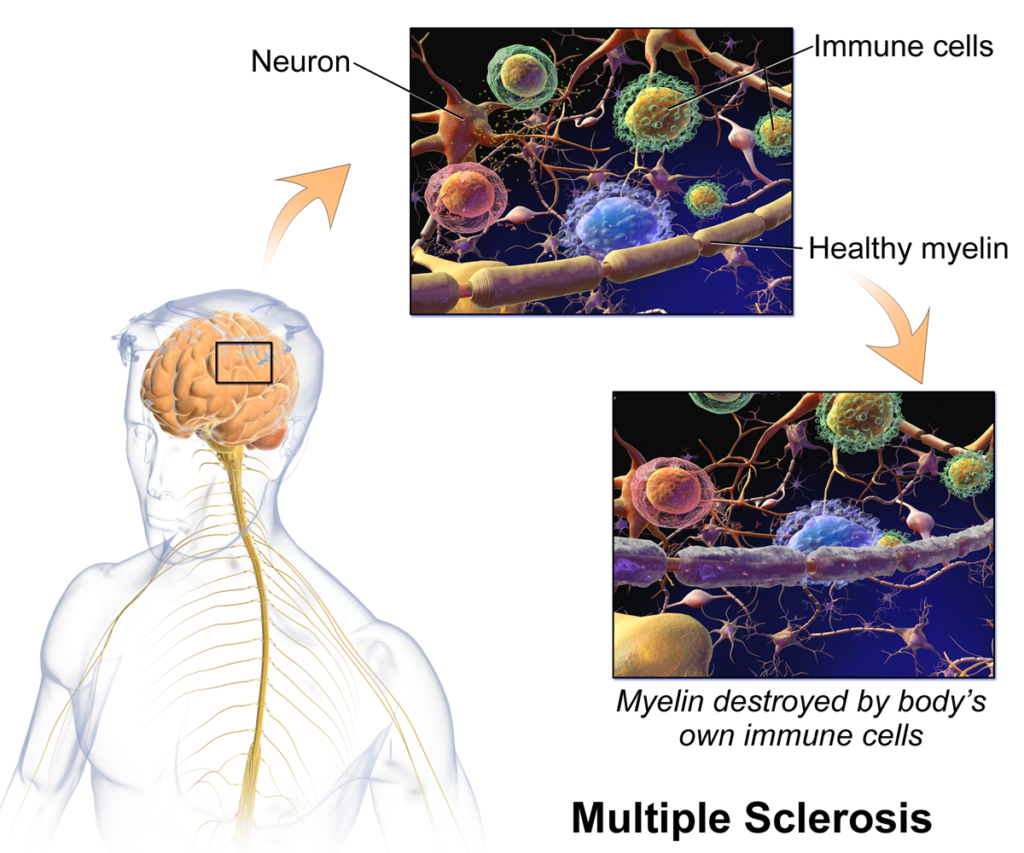
- Immune System Abnormalities: MS is thought to occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the protective covering of nerve fibers in the central nervous system.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Low levels of vitamin D have been linked to an increased risk of developing MS.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing MS, as well as a more severe progression of the disease.
Although the exact cause of Multiple Sclerosis is still unknown, researchers are working to better understand the underlying mechanisms of the disease. This information will hopefully lead to more effective treatments and ultimately, a cure for MS.
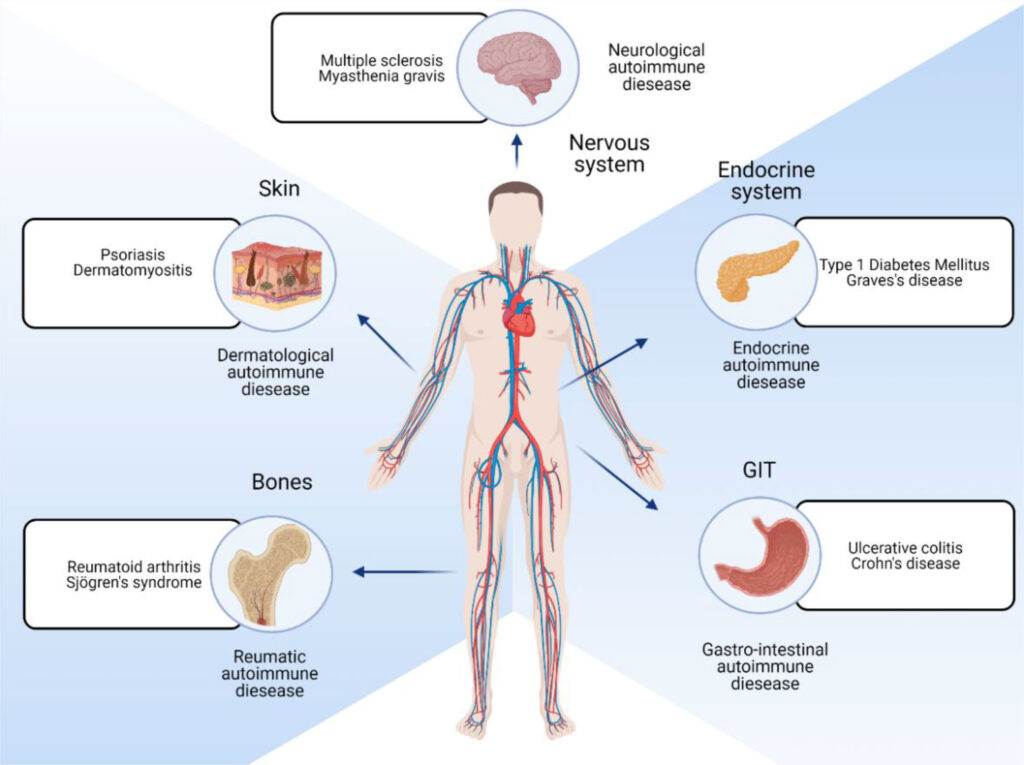
It’s important to note that MS is not contagious, and there is no evidence to suggest that it is caused by a particular lifestyle or diet. If you have concerns about the causes of Multiple Sclerosis, it’s best to speak with a doctor or specialist who can provide you with more information and support.
Clinical Features
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a complex condition that affects the central nervous system, and can cause a wide range of symptoms and clinical features. Some of the most common clinical features of MS include:
- Relapsing-Remitting MS: This is the most common form of Multiple Sclerosis and is characterized by periods of symptoms followed by periods of remission.
- Progressive MS: This form of Multiple Sclerosis is characterized by a gradual worsening of symptoms over time, with no clear periods of remission.
- Motor Symptoms: MS can cause muscle weakness, spasms, and problems with coordination and balance.
- Sensory Symptoms: Multiple Sclerosis can cause numbness, tingling, and problems with touch and temperature sensitivity.
- Cognitive Symptoms: MS can affect memory, concentration, and other cognitive functions.
- Visual Symptoms: MS can cause vision problems, including double vision, partial blindness, and eye pain.
- Fatigue: MS can cause overwhelming fatigue, even after minimal physical activity.
- Mood Changes: Multiple Sclerosis can cause mood swings, depression, and anxiety.
It’s important to note that MS symptoms can vary greatly from person to person, and can range from mild to severe. A doctor or specialist can provide a proper diagnosis and help you better understand the specific clinical features and symptoms that you may be experiencing. With proper treatment and support, many individuals with MS are able to manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
Management
The management of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a long-term process that aims to reduce symptoms, slow the progression of the disease, and improve quality of life. Some of the most common strategies for managing MS include:
- Medications: A range of medications are available for treating Multiple Sclerosis, including disease-modifying drugs that can slow the progression of the disease and relieve symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve mobility, balance, and coordination, and may also reduce muscle spasms and weakness.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy can help individuals with MS learn new skills and adapt to changes in their abilities.
- Speech Therapy: Speech therapy can help individuals with MS who are experiencing communication difficulties.
- Cognitive and Behavioral Therapy: Cognitive and behavioral therapies can help individuals with MS manage cognitive symptoms, mood changes, and other behavioral issues.
- Assistive Devices: Assistive devices, such as wheelchairs, canes, and crutches, can help individuals with MS maintain independence and mobility.
- Diet and Exercise: A healthy diet and regular physical activity can help improve energy levels, reduce fatigue, and promote overall health.
It’s important to work with a healthcare team that includes a neurologist, physical therapist, occupational therapist, and other specialists to develop a comprehensive management plan that is tailored to your specific needs and goals. With proper care and support, many individuals with Multiple Sclerosis are able to maintain a good quality of life and continue to live fulfilling, active lives.
Prevention
Unfortunately, there is currently no known way to prevent Multiple Sclerosis (MS). However, researchers continue to study the causes and potential risk factors of the disease in an effort to find ways to prevent or delay its onset.
That being said, there are some steps that individuals can take to promote overall health and wellness, which may reduce the risk of developing MS or other chronic conditions. These steps include:
- Maintaining a healthy diet: Eating a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support overall health and reduce the risk of chronic disease.
- Getting regular physical activity: Regular physical activity has been shown to reduce the risk of developing MS, as well as improve physical function and overall health.
- Avoiding smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for many chronic conditions, including MS, and avoiding smoking or quitting smoking can greatly reduce the risk of developing the disease.
- Managing stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of chronic disease. Practicing stress management techniques, such as exercise, mindfulness, and therapy, can help reduce stress and improve overall health.
- Monitoring sun exposure: Low levels of vitamin D have been linked to an increased risk of developing MS. Monitoring sun exposure and getting adequate levels of vitamin D through food or supplements can help reduce the risk of developing the disease.
While these steps may not prevent the onset of Multiple Sclerosis, they can help promote overall health and well-being, and may reduce the risk of developing other chronic conditions. It’s important to talk to a doctor or specialist if you have concerns about your risk of developing MS or other health conditions.
Treatment
The treatment of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a complex and ongoing process that aims to reduce symptoms, slow the progression of the disease, and improve quality of life. There is no single treatment that works for everyone with MS, and the best approach will vary depending on the individual’s symptoms and needs.
The following are some of the most common treatment options for MS:
- Medications: A range of medications are available for treating MS, including disease-modifying drugs that can slow the progression of the disease and relieve symptoms. Some of the most commonly used disease-modifying drugs for Multiple Sclerosis include interferons, glatiramer acetate, and natalizumab.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve mobility, balance, and coordination, and may also reduce muscle spasms and weakness.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy can help individuals with MS learn new skills and adapt to changes in their abilities.
- Speech Therapy: Speech therapy can help individuals with MS who are experiencing communication difficulties.
- Cognitive and Behavioral Therapy: Cognitive and behavioral therapies can help individuals with MS manage cognitive symptoms, mood changes, and other behavioral issues.
- Assistive Devices: Assistive devices, such as wheelchairs, canes, and crutches, can help individuals with MS maintain independence and mobility.
- Diet and Exercise: A healthy diet and regular physical activity can help improve energy levels, reduce fatigue, and promote overall health.
It’s important to work with a healthcare team that includes a neurologist, physical therapist, occupational therapist, and other specialists to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs and goals. With proper care and support, many individuals with Multiple Sclerosis are able to manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
Medications
Medications play a crucial role in the treatment of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). They can help relieve symptoms, slow the progression of the disease, and improve overall quality of life. The specific medications used to treat MS will depend on the individual’s symptoms, the type and stage of the disease, and other factors.

The following are some of the most common medications used to treat MS:
- Disease-Modifying Drugs (DMDs): DMDs are the primary medications used to treat Multiple Sclerosis. They can slow the progression of the disease and reduce the frequency and severity of relapses. Some of the most commonly used DMDs for MS include interferons, glatiramer acetate, and natalizumab.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids are often used to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms during relapses. They are typically given intravenously and can be very effective in reducing the severity and duration of relapses.
- Muscle Relaxants: Muscle relaxants, such as baclofen and tizanidine, can help relieve muscle spasms and improve mobility.
- Pain Medications: Pain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and acetaminophen, can help relieve pain and discomfort associated with MS.
- Antidepressants: Antidepressants can help relieve depression, anxiety, and other mood changes that may be associated with Multiple Sclerosis.
- Anti-Anxiety Medications: Anti-anxiety medications, such as benzodiazepines, can help relieve anxiety and promote relaxation.
It’s important to work with a healthcare team to determine the best medications for your specific symptoms and needs. Some medications may cause side effects, so it’s important to monitor your symptoms and communicate any concerns to your healthcare team. With proper treatment, many individuals with MS are able to manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
Conclusion
There is no cure for MS, but treatment can help relieve symptoms, slow the progression of the disease, and improve overall quality of life. Medications, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and other treatments can all play a role in managing the symptoms of MS.

It can cause a range of symptoms, including muscle weakness, numbness, and difficulties with coordination and balance. The exact cause of MS is still unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
It’s important to work with a healthcare team that includes a neurologist and other specialists to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs and goals. With proper care and support, many individuals with MS are able to manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
In conclusion, Multiple Sclerosis is a complex condition that requires ongoing care and management. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments for MS, individuals with MS and their families can work together with their healthcare team to achieve the best possible outcomes.
watch some stories related to latest health news and updates here !
