
Introduction
Amputation is the surgical removal of a limb or part of a limb, typically as a result of injury, infection, or disease. The procedure can be traumatic for both the patient and their loved ones, and it is important to understand the reasons for amputation, the procedure itself, and the recovery process. This article will provide an overview of amputation and its aftermath, including the causes of amputation, the types of amputation, the surgical procedure, and the rehabilitation process.
Causes of Amputation
It is typically performed as a last resort, after other treatments have failed to improve the patient’s condition. Common causes of amputation are :
Trauma: Injury to a limb can lead to this condition if the injury is severe enough. This can include injuries caused by accidents, such as car crashes or industrial accidents, or injuries caused by violence, such as gunshots or bombings.
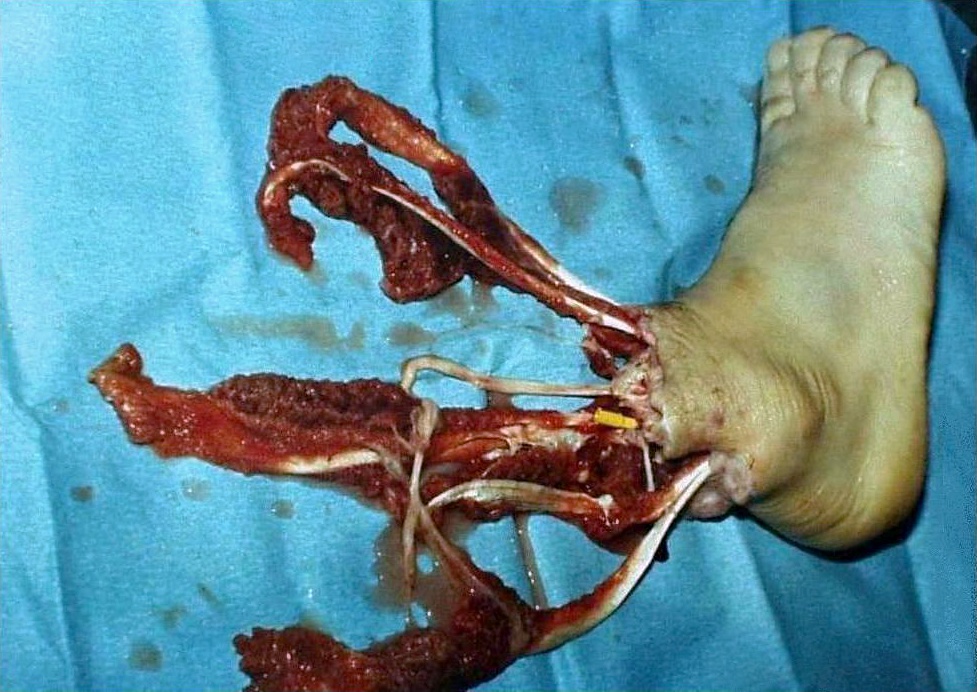
Peripheral artery disease (PAD): PAD is a condition in which the blood vessels in the legs become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the legs. If the condition becomes severe enough, this condition may be necessary to prevent gangrene (tissue death) from occurring.
Diabetes: People with diabetes are at increased risk of developing foot and leg problems, including infections, sores, and ulcers. If these conditions are not treated properly, this condition may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection.
Cancer: In some cases, amputation may be necessary to remove a tumor or cancerous growth in a limb.
Types of Amputation
There are several different types of amputation, depending on the location and extent of the limb that is being removed. Common amputation types are :
Trans-tibial amputation: This type of this condition involves the removal of the foot and ankle, with the knee joint remaining intact.
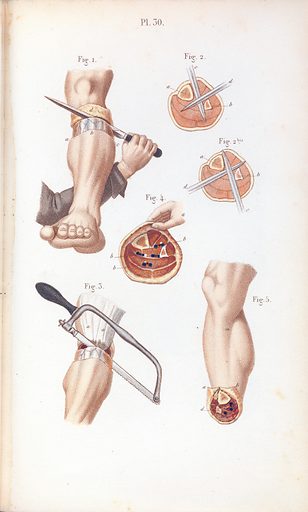
Trans-femoral amputation: This type of this condition involves the removal of the leg, including the thigh bone (femur), knee joint, and part of the lower leg.
Above-knee amputation: This type of this condition involves the removal of the leg, including the thigh bone, knee joint, and most of the lower leg.
Below-elbow amputation: This type of this condition involves the removal of the arm, including the part of the arm from the elbow to the hand.
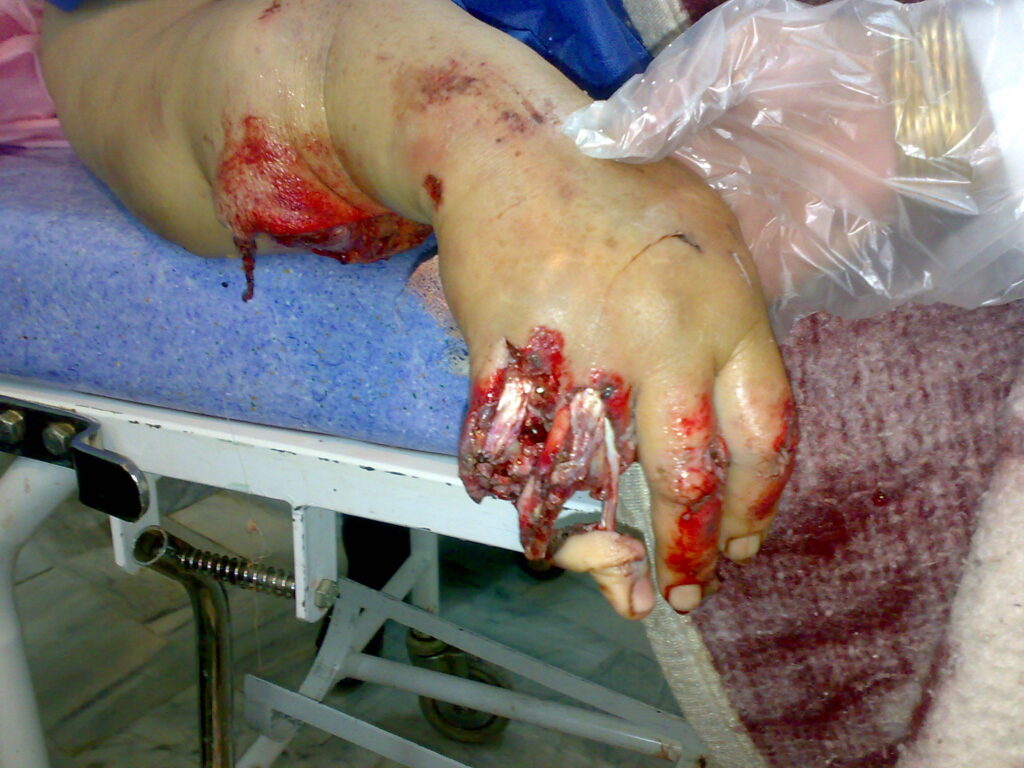
Above-elbow amputation: This type of this condition involves the removal of the arm, including the part of the arm from the shoulder to the elbow.
Surgical Procedure
The surgical procedure for amputation will vary depending on the type of this condition that is being performed. In general ,This will involve these steps :
Anesthesia: The patient will be given general anesthesia to prevent pain during the surgery.
Incision: The surgeon will make an incision through the skin and muscle, exposing the bones in the limb.
Bone cutting: The bones in the limb will be cut using a saw.
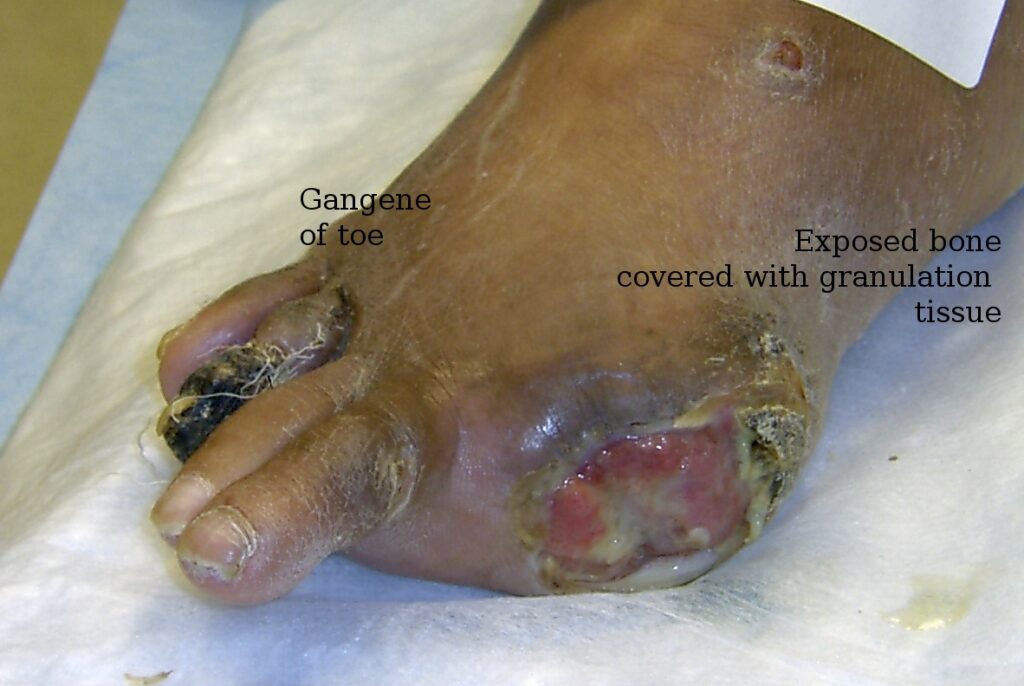
Stump preparation: The remaining part of the limb, called the stump, will be prepared for the fitting of a prosthetic.
Closure: Sutures will close the incision.
Dressings and bandages: The amputation site will be covered with dressings and bandages to promote healing.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery process after this condition can be long and challenging, and it is important for the patient to have a strong support system in place. The recovery process can be broken down into several stages:
Acute phase: This is the immediate period following surgery, when the patient is recovering from the procedure. The patient will be in the hospital for several days, and will be closely monitored for any complications, such as infection.
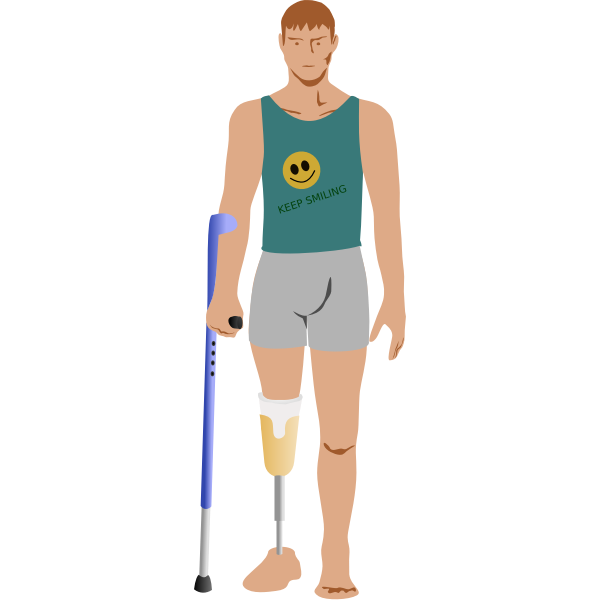
Rehabilitation phase: The patient will begin physical therapy and rehabilitation to help them adjust to their new limb status. This will involve exercises to help the patient regain strength, flexibility, and mobility. The patient will also learn how to use any assistive devices, such as crutches or a wheelchair, that they may need.
Prosthetic phase: Once the patient has recovered enough, they will be fitted with a prosthetic limb. This will involve several fittings and adjustments to ensure a proper fit. The patient will also need to learn how to use the prosthetic, which can take some time and practice.

Long-term follow-up: The patient will need to continue to see their healthcare provider for regular follow-up appointments. This will involve monitoring the amputation site for any complications, such as infection or skin breakdown, and adjusting the prosthetic as needed.
Read about amputation on wikipedia here !
Conclusion
This condition can be a traumatic and life-changing event, but with proper care and support, patients can learn to adjust and live a fulfilling life. Understanding the causes, types, surgical procedure, and recovery process can help patients and their loved ones prepare for the journey ahead.

It’s important to have a multidisciplinary team approach involving surgeons, physical therapists, prosthetist, psychologist and others to ensure the best possible outcome. With the right care and support, patients can learn to live with their condition and continue to lead fulfilling lives.
